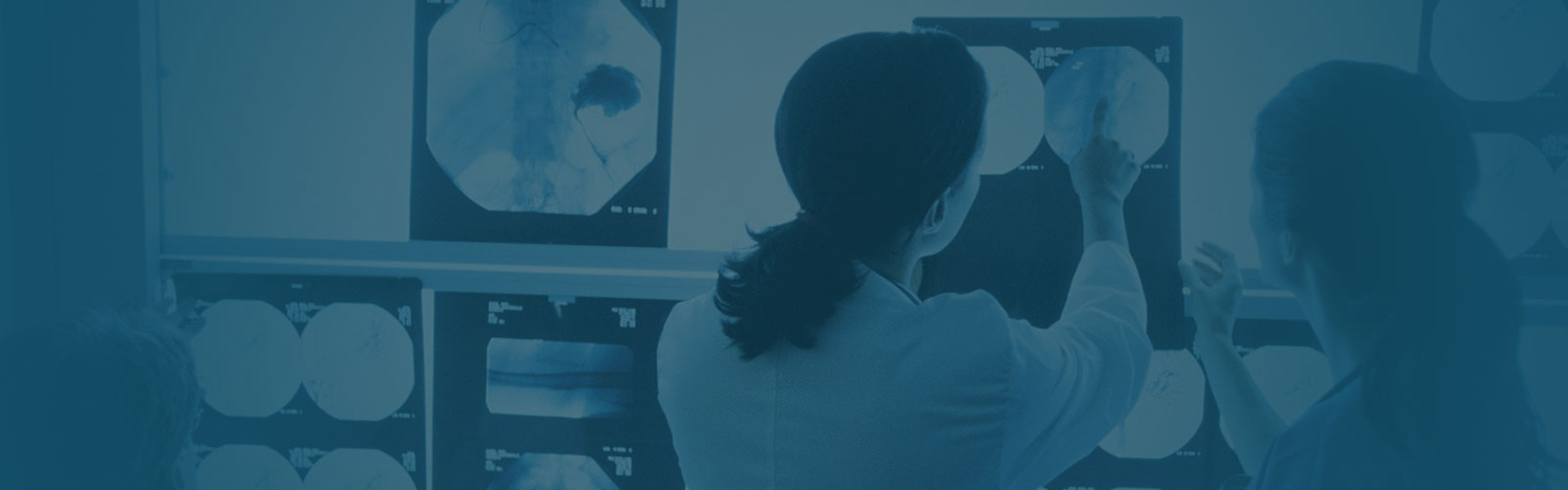
Our Musculoskeletal Imaging Centers
Founded in 1984, RadNet has 30 years of experience providing high-quality, cost-effective imaging services. With more than 250 outpatient imaging centers spread across 6 states, RadNet serves large, diverse sets of patient populations and works with physicians practicing in various medical specialties.
Through this network, RadNet provides a full range of screening, diagnostic and interventional procedures to meet numerous imaging needs. This requires a large team of board-certified radiologists with advanced training in and knowledge of various medical sub-specialties, as well as centers equipped with some of the most state-of-the-art imaging equipment available.
Musculoskeletal Imaging at Our Centers
Musculoskeletal imaging is one of the fastest growing fields in medicine. Working with health care professionals in sports medicine, orthopaedics, rheumatology, oncology and pathology, musculoskeletal imaging specialists must maintain current clinical knowledge across a range of specialties and imaging modalities.
Musculoskeletal imaging refers to the science and practice of examining bones, joints and soft tissues using equipment including conventional X-ray, computed tomography (CT), ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Musculoskeletal imaging specialists require advanced knowledge of structural anatomy and numerous health conditions, including chronic pain, fibromyalgia, rheumatoid arthritis and bone cancer, among others.
![]()
Musculoskeletal Imaging Technologies
RadNet is committed to tracking developments in various medical imaging technologies and strives to maintain facilities equipped with state-of-the-art equipment. Within the musculoskeletal imaging sub-specialty, there are numerous diagnostic and interventional procedures that can be performed with several different imaging modalities.
Advanced imaging technologies that patients and physicians can expect to find at some RadNet centers include 3T MRI and multi-slice CT.
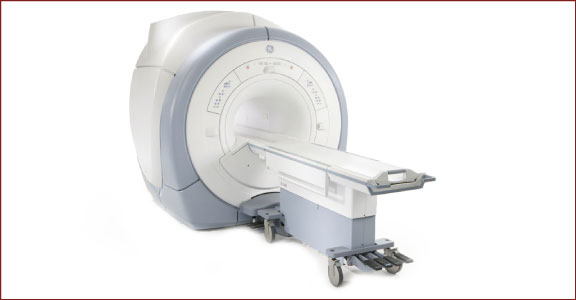
3T MRI
Advancements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) over the past several decades have made it one of the more valuable modalities to musculoskeletal imaging specialists. Unlike many imaging modalities, MRI does not use radiation to produce images of internal body structures and organs. Instead, magnets are used to track radiofrequency signals as they travel through the body and specialized computer software translates these movements into images.
More powerful magnets, or those with a higher field strength, produce more detailed images. A unit of measurement called ‘Teslas’ (T) is used to indicate the field strength of an MRI machine. Currently, 3T MRI represent the most powerful MRI machines available in clinical settings.
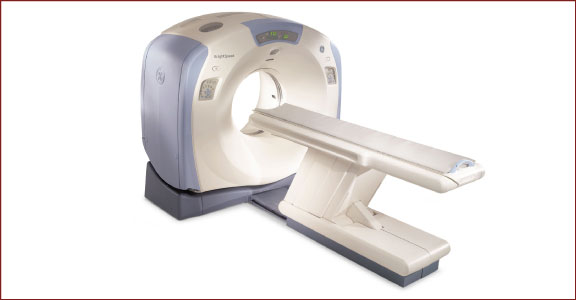
Multi-slice CT
Computed tomography (CT) produces multiple X-ray images of internal body structures from multiple angles. Each image captures a thin slice of the body. Radiologists can view individual slices, as if flipping through the pages of a book, or they can be digitally processed to create cross-sectional views and three-dimensional representations of the area of the body being examined.
Multi-slice CT machines, such as 16-slice and 64-slice machines, produce thinner slices than conventional CT. In addition to capturing more detail than conventional CT machines, multi-slice CT also offers reduced radiation exposure and shorter exam times.

